When it comes to managing your finances, the terms financial advisor and financial planner are often used interchangeably. However, they refer to two distinct types of professionals who offer different services. Understanding the difference between these roles is crucial for anyone seeking financial guidance.
Hook: The Importance of Financial Planning

Did you know that only 30% of Americans have a long-term financial plan? This statistic highlights the importance of financial planning and the need for professional guidance to secure your financial future.
Definition of Terms

A financial advisor is a professional who provides advice on various financial matters, including investments, tax laws, and insurance. On the other hand, a financial planner takes a more comprehensive approach, helping clients create long-term financial strategies that encompass all aspects of their financial lives.
Importance of Understanding the Difference
Knowing the distinction between a financial advisor and a financial planner can help you choose the right professional to meet your unique financial needs. Whether you need specific investment advice or a comprehensive financial plan, understanding these roles will guide you in making an informed decision.
Thesis Statement

In this article, we will explore the differences between financial advisors and financial planners, their roles, services, qualifications, and when to choose one over the other. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of which professional is best suited for your financial needs.
Section 1: Understanding Financial Advisors
1.1 Definition of a Financial Advisor

A financial advisor is a professional who offers advice and direction on various financial matters, primarily focusing on managing investments. They help clients make informed decisions to build wealth and achieve their financial goals.
Types of Financial Advisors

Financial advisors can specialize in different areas, including:
- Investment Advisors: Focus on managing investment portfolios.
- Wealth Managers: Provide comprehensive financial services, including investment management, estate planning, and tax planning.
1.2 Services Offered by Financial Advisors

Investment Management
Financial advisors manage investment portfolios, helping clients choose the right assets to invest in based on their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Retirement Planning

Advisors assist clients in planning for retirement by developing strategies to save and invest for long-term financial security.
Tax Planning

They offer tax optimization strategies to minimize tax liabilities and maximize returns on investments.
Insurance Advice

Advisors provide guidance on risk management and insurance, ensuring clients are adequately protected against unforeseen events.
1.3 Qualifications and Credentials

Licensing Requirements
Financial advisors must pass specific licensing exams, such as the Series 7 and Series 65, to offer investment advice and manage securities.
Professional Designations
Many financial advisors hold certifications like the Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA) or Certified Financial Planner (CFP), which require rigorous education and ethical standards.
Section 2: Understanding Financial Planners

2.1 Definition of a Financial Planner
A financial planner is a professional who helps individuals and organizations create strategies to meet long-term financial goals. They take a holistic approach, considering all aspects of a client’s financial life.
2.2 Services Offered by Financial Planners

Comprehensive Financial Planning
Financial planners assist with budgeting, cash flow analysis, and goal setting, providing a roadmap for achieving financial stability.
Retirement Planning
They develop detailed strategies for long-term financial security, ensuring clients are well-prepared for retirement.
Estate Planning

Planners help clients with wills, trusts, and legacy planning, ensuring their assets are distributed according to their wishes.
Education Funding
They assist in planning for children’s education expenses, helping clients save and invest for future educational needs.
2.3 Qualifications and Credentials

Licensing Requirements
Financial planners must pass exams and meet continuing education requirements to maintain their certifications.
Professional Designations
The Certified Financial Planner (CFP) designation is highly regarded and requires extensive education, experience, and ethical standards.
Section 3: Key Differences Between Financial Advisors and Financial Planners
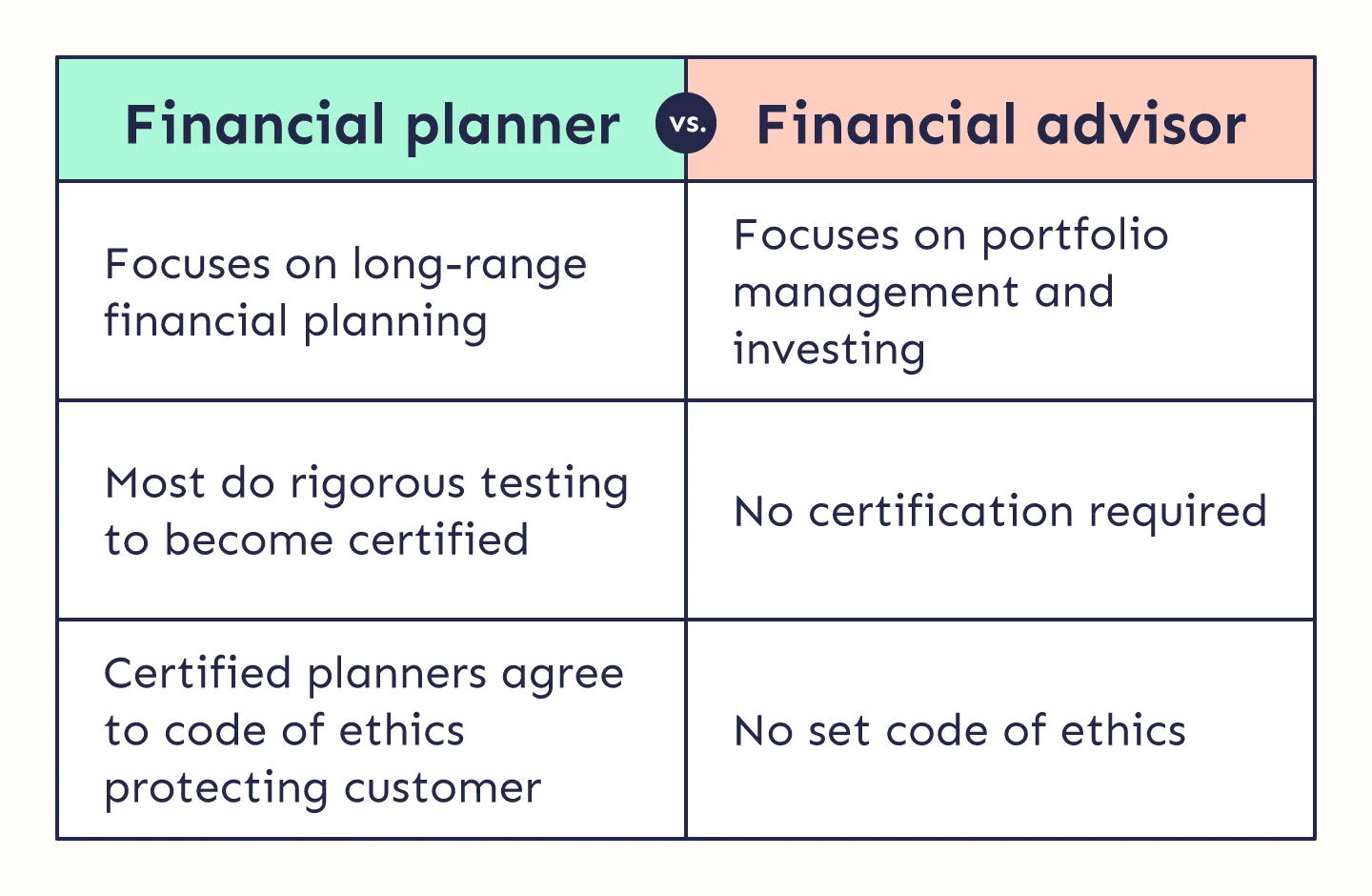
3.1 Scope of Services
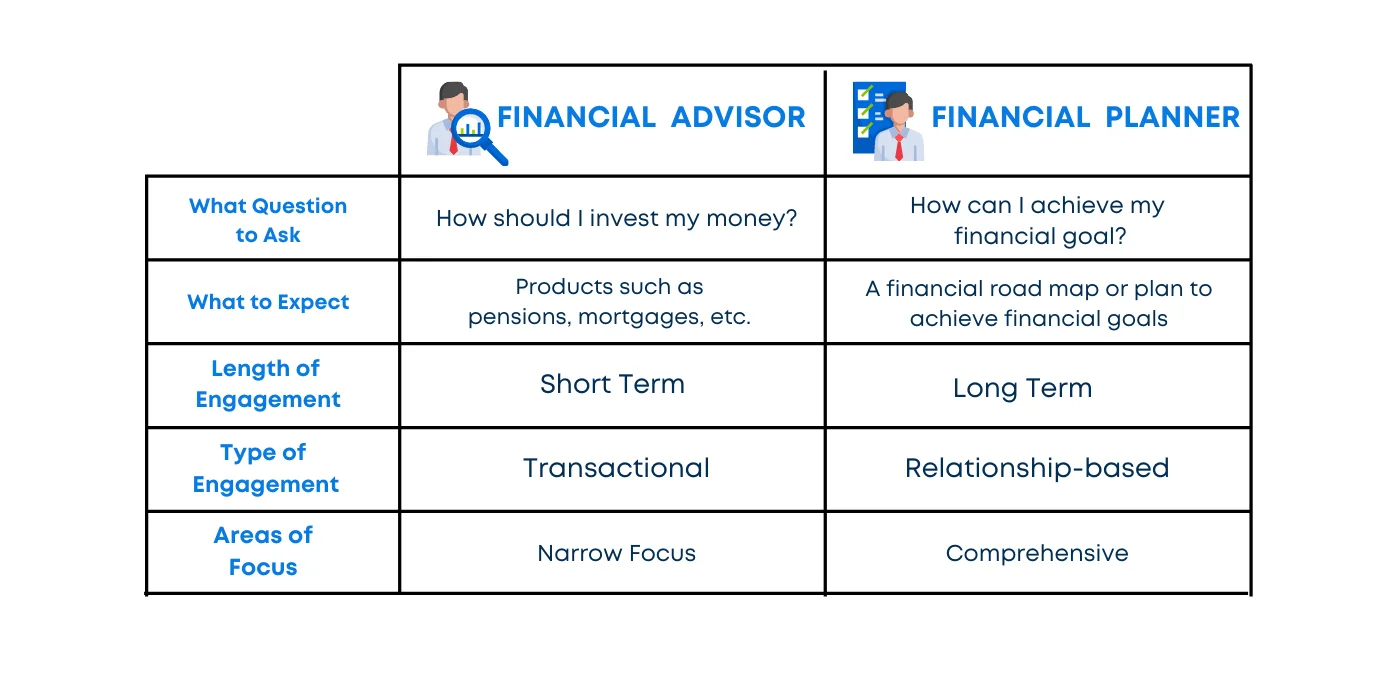
Narrow vs. Broad Focus
Financial advisors typically focus on specific financial areas like investments, while financial planners offer comprehensive services that cover all aspects of a client’s financial life.
3.2 Approach to Financial Management
Transactional vs. Holistic
Advisors often take a transactional approach, providing specific advice on investments. In contrast, planners adopt a holistic approach, considering the client’s entire financial picture.
3.3 Client Relationships

Ongoing Support vs. One-Time Advice
Financial planners usually establish long-term relationships with clients, offering ongoing support and regular check-ins. Financial advisors may provide one-time advice or periodic consultations.
3.4 Fee Structures

Commission-Based vs. Fee-Only
Financial advisors may earn commissions on the products they sell, while financial planners typically charge flat fees or hourly rates. Understanding these fee structures is crucial for clients to know what they are paying for.
Section 4: When to Choose a Financial Advisor vs. a Financial Planner
4.1 Situations Ideal for Financial Advisors
Investment-Focused Goals

If your primary goal is to manage investments and grow your portfolio, a financial advisor is the right choice.
Short-Term Financial Needs
For quick, tactical advice on specific financial matters, a financial advisor can provide the necessary guidance.
4.2 Situations Ideal for Financial Planners
Comprehensive Financial Goals
When you need a holistic approach to manage all aspects of your financial life, a financial planner is more suitable.
Life Changes
Major life events like marriage, inheritance, or retirement require extensive planning, making a financial planner the ideal choice.
Section 5: How to Choose the Right Professional for Your Needs
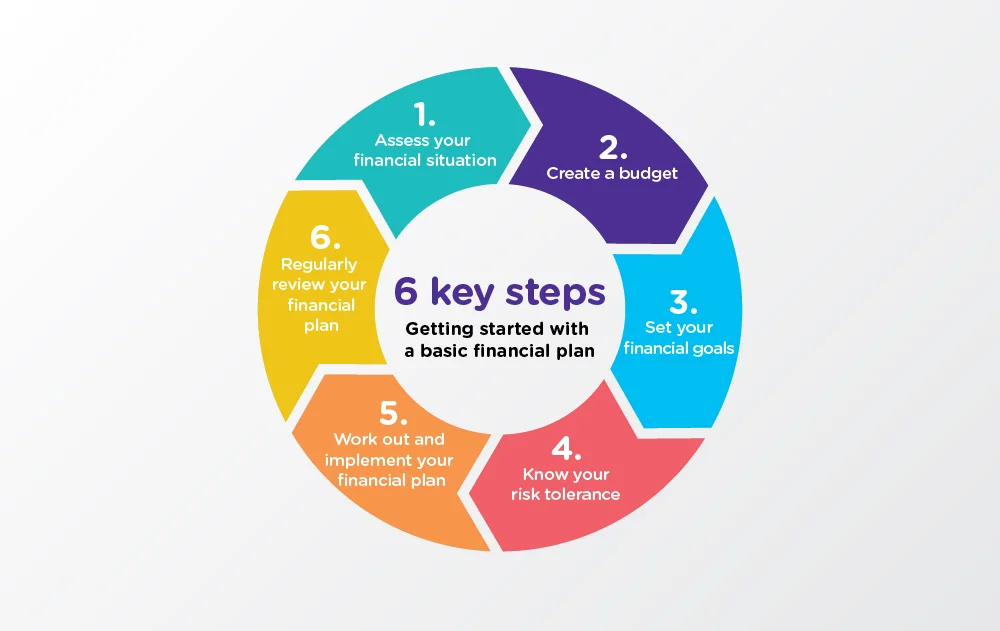
5.1 Assessing Your Financial Situation
Self-Assessment
Before seeking professional help, assess your financial situation by asking yourself key questions about your financial goals and needs.
Identifying Goals
Understanding your financial goals is crucial in determining whether you need a financial advisor or a planner.
5.2 Researching Professionals
Finding Qualified Advisors and Planners

Use online resources and tools to search for qualified professionals in your area. Look for those with relevant certifications and experience.
Checking Credentials and Reviews
Verify the credentials and reviews of potential advisors or planners to ensure they are qualified and reputable.
5.3 Initial Consultations

What to Expect
During the initial consultation, the professional will assess your financial situation and discuss how they can help you achieve your goals.
Questions to Ask
Prepare a list of questions to ask during the consultation to determine if the professional is the right fit for your needs.